Cycling. Health. Covid. Diet.
- Thread starter GLJoe
- Start date
The British Sleep Society position statement on Daylight Saving Time in the UK
‘Unprecedented risk’ to life on Earth: Scientists call for halt on ‘mirror life’ microbe research
Experts warn that mirror bacteria, constructed from mirror images of molecules found in nature, could put humans, animals and plants at risk of lethal infections
"Although a viable mirror microbe would probably take at least a decade to build, a new risk assessment raised such serious concerns about the organisms that the 38-strong group urged scientists to stop work towards the goal and asked funders to make clear they will no longer support the research. "
“The threat we’re talking about is unprecedented,” said Prof Vaughn Cooper, an evolutionary biologist at the University of Pittsburgh. “Mirror bacteria would likely evade many human, animal and plant immune system responses and in each case would cause lethal infections that would spread without check.”
Experts warn that mirror bacteria, constructed from mirror images of molecules found in nature, could put humans, animals and plants at risk of lethal infections
"Although a viable mirror microbe would probably take at least a decade to build, a new risk assessment raised such serious concerns about the organisms that the 38-strong group urged scientists to stop work towards the goal and asked funders to make clear they will no longer support the research. "
“The threat we’re talking about is unprecedented,” said Prof Vaughn Cooper, an evolutionary biologist at the University of Pittsburgh. “Mirror bacteria would likely evade many human, animal and plant immune system responses and in each case would cause lethal infections that would spread without check.”
Bowel cancer rising among under-50s worldwide, research finds
Study suggests rate of disease among young adults is rising for first time and England has one of the fastest increases
Study suggests rate of disease among young adults is rising for first time and England has one of the fastest increases
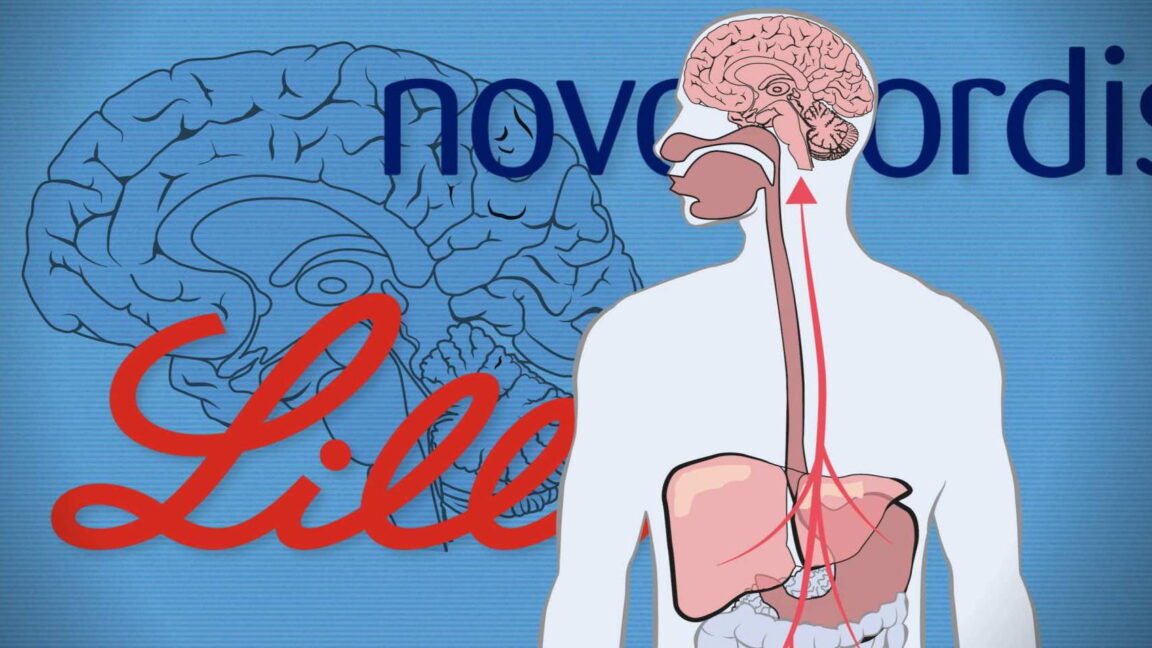
Weight loss drugs may also treat addiction, Alzheimer’s, and heart disease
Pharmaceutical companies are already cashing in on their other health benefits.
 arstechnica.com
arstechnica.com
Pharmaceutical companies are already cashing in on their other health benefits.

Weight loss drugs may also treat addiction, Alzheimer’s, and heart disease
Pharmaceutical companies are already cashing in on their other health benefits.
 arstechnica.com
arstechnica.com
Do people reach 100 by surviving, delaying, or avoiding diseases? A life course comparison of centenarians and non-centenarians from the same birth cohorts
Why hasn’t the bird flu pandemic started?
Some scientists examining mutations found in H5N1 viruses fear major outbreak is imminent but others say pathogen remains unpredictable
"So why hasn’t H5N1 touched off a pandemic yet?
One simple answer is that the virus may just need more time to hit the right combination of mutations. The high mutation rate of influenza viruses should tip the odds in H5N1’s favor: “My rule of thumb is that one in 4000 [virus] particles will have a mutation at the amino acid that you are interested in,” Paulson says. Indeed, one polymerase mutation the virus likely needs, dubbed 627K because it leads to the amino acid lysine (K) at position 627 of the protein, has been found several times in strains infecting mammals but also in virus isolated from the first human case associated with the U.S. outbreak in dairy cows."
Some scientists examining mutations found in H5N1 viruses fear major outbreak is imminent but others say pathogen remains unpredictable
"So why hasn’t H5N1 touched off a pandemic yet?
One simple answer is that the virus may just need more time to hit the right combination of mutations. The high mutation rate of influenza viruses should tip the odds in H5N1’s favor: “My rule of thumb is that one in 4000 [virus] particles will have a mutation at the amino acid that you are interested in,” Paulson says. Indeed, one polymerase mutation the virus likely needs, dubbed 627K because it leads to the amino acid lysine (K) at position 627 of the protein, has been found several times in strains infecting mammals but also in virus isolated from the first human case associated with the U.S. outbreak in dairy cows."
How BioNTech’s “revolutionary” lung cancer vaccine actually works
The promising new treatment builds on research that went into developing COVID vaccines.

 bigthink.com
bigthink.com
The promising new treatment builds on research that went into developing COVID vaccines.

How BioNTech’s "revolutionary" lung cancer vaccine actually works
The promising new lung cancer treatment builds on the research that went into developing coronavirus vaccines during the pandemic.
Dietary fructose enhances tumour growth indirectly via interorgan lipid transfer
Sold-out farm shops, smuggled deliveries and safety warnings: US battle over raw milk grows
Unpasteurised milk, seen as both anti-government and anti-corporate, soars in popularity among conspiracy theorists and new agers
Unpasteurised milk, seen as both anti-government and anti-corporate, soars in popularity among conspiracy theorists and new agers
The Real Appeal of Raw Milk
Not even bird flu can stop some Americans’ thirst for unpasteurized dairy.
 www.theatlantic.com
www.theatlantic.com
Not even bird flu can stop some Americans’ thirst for unpasteurized dairy.

The Real Appeal of Raw Milk
Not even bird flu can stop some Americans’ thirst for unpasteurized dairy.
Don't throw away your printed books: A meta-analysis on the effects of reading media on reading comprehension
Brain stimulation helps partially paralyzed patients walk again

 newatlas.com
newatlas.com

Brain stimulation helps partially paralyzed patients walk again
Two patients with spinal injuries have seen improvements in their ability to walk again, thanks to deep brain stimulation (DBS). Intriguingly, the therapy targets a region of the brain that normally isn’t associated with motor skills.
Health Officials Investigate Rare Form of Blindness Tied to Ozempic
Several recent studies have found a possible connection between semaglutide use and a rare condition that causes sudden vision loss.

 gizmodo.com
gizmodo.com
Several recent studies have found a possible connection between semaglutide use and a rare condition that causes sudden vision loss.

Health Officials Investigate Rare Form of Blindness Tied to Ozempic
Several recent studies have found a possible connection between semaglutide use and a rare condition that causes sudden vision loss.
G
Ghost1951
Guest
Just buy a small bowl, cook all your food yourself from sensible ingredients, have only 3 meals a day and NEVER eat more than what fits in your bowl.
There is a reason that most adults in the UK are now overweight or obese. It was not the case fifty years ago, or more so sixty years ago. Portion sizes have got much bigger, and people eat huge, calorific take aways and processed food.
You won't need ozempic if you do this.
There is a reason that most adults in the UK are now overweight or obese. It was not the case fifty years ago, or more so sixty years ago. Portion sizes have got much bigger, and people eat huge, calorific take aways and processed food.
You won't need ozempic if you do this.

Advice accepted on spring 2025 COVID-19 vaccination programme
The government has accepted advice from the Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation (JCVI) for the spring 2025 COVID-19 vaccination programme.
We as a society are also far more sedentary than we were 50-60 years ago. We used to walk & cycle but now we use the car.Just buy a small bowl, cook all your food yourself from sensible ingredients, have only 3 meals a day and NEVER eat more than what fits in your bowl.
There is a reason that most adults in the UK are now overweight or obese. It was not the case fifty years ago, or more so sixty years ago. Portion sizes have got much bigger, and people eat huge, calorific take aways and processed food.
You won't need ozempic if you do this.
G
Ghost1951
Guest
Indeed - that is true and contributes to poor cardio vascular health. Exercise has more benefits than that too- especially for psychological well being.We as a society are also far more sedentary than we were 50-60 years ago. We used to walk & cycle but now we use the car.
In the context of the current point about weight loss though, I maintain that it is not possible (for an ordinary person) to make significant inroads to losing weight through exercise alone. You have to cut consumption to make big inroads into reducing over-weight. If you have the time to march twenty-miles a day - fine - if you don't eat more to compensate for the exercise, you will lose weight, but most people can't do that, so smaller portions and hunger are the only way.
A ten years ago - I walked the Camino de Santiago in Spain. It is 490 miles of walking, uphill into mountains and down dale across plains and vineyards. Walking 15 - 20 miles a day you lose weight, but it is a massive output of energy.


Last edited by a moderator:
In my experience, calorie restriction with slow jogging is a brutal but effective weight loss method, it all falls away fast. Says here slow jogging for an hour burns 800 calories, I reckon that's about right. But it is brutal - I kept that combination up for a couple of weeks, then reverted to intermittent fasting only, less painful. These days I either slow jog or restrict calories, alternate weeks. Takes a special type of guy with a will of iron.
Last edited:
Related Articles
-
 MTF Enterprises announces acquisition of EMU Electric Bikes
MTF Enterprises announces acquisition of EMU Electric Bikes- Started by: Pedelecs
-
 Wisper 806T folding bike wins Which? ‘Best Buy’
Wisper 806T folding bike wins Which? ‘Best Buy’- Started by: Pedelecs
-
 Sustrans calls for protected cycle lanes
Sustrans calls for protected cycle lanes- Started by: Pedelecs
-
 Amazon launch their first UK e-cargo micromobility hub
Amazon launch their first UK e-cargo micromobility hub- Started by: Pedelecs




